
The eradication of smallpox illustrates the success of a proactive worldwide policy.

Starting in the autumn of 1889, a strange illness strikes Western populations: the Asiatic or Russian Flu.

Overeaters Anonymous is a therapeutic offer, both alternative and spiritual, aimed at people suffering from eating disorders.

In 1800, in the cause of health and public order, General Menou decrees the first French ban on the consumption of cannabis.

Considered one of the theatres of the Third Reich’s euthanasia program Am Spiegelgrund is a space where Nazi impact on paedopsychiatry is on display.

There is today a growing clamour for the democratisation of vasectomy but this voluntary sterilisation practice was already in full swing in !8th century Russia.

In psychiatric institutions, clothing is a tool uniformizing the patients and the hospital staff in support of therapeutics, hygiene and order.

The public notoriety of the “morphinée" at the end or the 19th century is a testament to the political and professional issues at play as categories were being devised regarding substance abuse.

The overlooked health provision of public baths retraces for us the history of body hygiene and the inequalities it portends.

Between the 15th and the 19th century, Venice’s reformed its quarantine system on the lazaretto model in view of its unequal successes in dealing with plague epidemics.

For centuries, sexuality was deemed to answer the need to procreate rather than the call of desire, making of onanism a mortal sin.

In the collective mindscape, embalming is attached to Ancient Egypt. Such practices were part and parcel of mummification and that era’s funerary practices. They permitted the preservation of the deceased’s body prior to its inhumation. It should therefore come as no surprise that the art of thanatopraxis met with renewed interest in the 18th and 19th centuries.

More than a simple symbol, the caduceus, inherited from Antiquity, became the emblem of pharmacy as we know it today.

The surgical or prophylactic mask was mainstreamed against the background of brutal epidemic episodes (Third Plague Pandemic, “Spanish flu”…) which kickstarted the development of public protection policies against diseases.

"Subtle energies" is a key term in today’s alternative medicine. It plays a central role in the area of energy healing, which includes therapies such as acupuncture, Reiki, Pranic Healing, and Therapeutic Touch.

The history of anti-drug campaigns in Canada brings out the equal parts played by international politics and public health concerns.

Scientific dream theories – as well as traditional oneirocritical discourses – have long kept dreaming outside the historical field.

The hookworm causes a parasitic infection the history of which helps show how the Rockefeller Foundation impacted on the United States federal healthcare provisions.

Ever since Freud, psychoanalysis has taken an interest in the psychic life of Children. First considered a minor practice, psychoanalysis with children reached its full dimension in the 1970s.

The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) is a nosological classification that has played - and continues to play - a key role in structuring psychiatric care and research.

The health crisis linked to the Covid-19 epidemic has given a new impetus to the development of mental health care provision via teleconsultations.

The European nationalisms have hindered the research on the most mysterious disease of the 20th century.

The appearance of new syringe models in the 1850s questions the conditions of the development of medical techniques.

There are policies of the dream, as illustrated by the different ways of apprehending the dreams in the Amerindian populations.

Over two centuries, medical, political and social circles around the world have been debating the stakes of the fight against alcoholism.

During the «Great Depression» of the 1930s, psychiatric professionals diagnosed a new disease: the «psychosis of current events».

The American psychiatric classification was once a tool at the service of white political power to the detriment of the emancipation of African-Americans.

Patients and physicians hold conflicting political and scientific views on the existence of an emerging disease caused by tick bites.

Human dissections have been an essential part of medicine since the fourth century B.C. Contrary to widely held belief, the Church did not prohibit them in the Middle Ages.

In 1961, the publication of an ex-internee’s memoir instigated a mental health policy reform in the State of Quebec.

The bed is not a simple object structuring the hospital space. It is also a therapeutic instrument and an indicator for public authorities to guide hospital policy.

In 1804, the outbreak of a suspicious disease in Livorno led to strong tensions between the Italian states.

Eclipsed by the rise of antibiotics after the Second World War, can bacteria-eating viruses discovered at the beginning of the 20th century be therapeutic tools while resistance to antibiotic therapy emerges?

Dr Quinn, Medicine Woman can be considered as a feminist series as it highlights women's access to scientific and medical professions

The history of “menopause” as a medical category revolves around gender relationships.

How does the history of epilepsy explain the negative image that this disease still sometimes suffers from?

The Hollywood smile, characterized by white, straight teeth, is a complex phenomenon involving social, cultural, scientific and technological changes in the early 20th century. It emerged with the development of film, advertising, orthodontics and cosmetic dentistry.
The medical supervision of anorexia responded to political and scientific stakes in order to normalize puberty.

In the 19th century, nostalgia became a mortal illness that endangered French military and colonial might.

Devised to control the female body, the corset has had, between the 18th and the 20th century, many detractors.

Can an Eastern spiritual practice become a Western health practice without betraying itself?

The naturalness of breast feeding has been subordinated to a political idea of the Nation asserted in an explicit hierarchisation of class and race.

In Haïti, some individuals come back to life whereas they had been declared dead then inhumed.

The topicality of cases of infanticide invites us to question the historical origin of the madness of motherhood.

The relationship to sugar in our society is sustainably anchored on a difference between genders.

Knowledge of the interconnection of the gut and psyche has a longer history than scientists often admit.

Time-measurement devices in clinical and experimental settings have historically tended to pathologize mental “slowness” and normalize “speed” as a signifier of mental health.

“Ex-GI becomes blonde beauty” : in 1953, Christine Jorgensen became the first transsexual in the media.

Around 1900, a vegetarian movement was organized in France to resolve the social question.

In the mid-1970s, the near-death experience emerged as a new spiritual manifestation within medicine, at the heart of a policy of survivors and their trauma.
_max100x100.jpg?objectId=defaultWebContent://bcbad9d9-7641-4f41-80e0-ad73c94aec29)
The 1821 yellow fever outbreak in Barcelona made clear the political dimensions of public health legislation.

Lesbianism is considered in the 17th and nineteenth19th centuries, both as a physical and behavioural pathology.

Does the Covid-19 health crisis mark the advent of telemedicine in our societies?

The naming of this syndrome in 1981 is loaded with potent political and historical implications.

The Gueules cassées, in other words facially disfigured soldiers, are recognized as war wounded people with difficulty, but they represent a turning point in surgery.

Suitcases as symbols of the struggle for dignity and civil rights of people with mental illnesses

The term psychedelic was coined to refer to psychotic substances explored for use in psychiatry, but which remain under strict control

The category of “rare diseases” was born of the interactions between authorities, patients and the pharmaceutical industry following a consolidation of US pharmaceutical legislation.

The re-naming of an illness is as much a political act as a scientific one, as shown by the case of lypemania

As early as the years 1930-50, tuberculosis patient associations became significant political actors.
(1)_max100x100.jpg?objectId=defaultWebContent://0094ad7f-085e-4b17-9afb-0e87436fc73b)
Tobacco control, for all that it serves unquestionable health purposes, remains steeped in political issues

The truth serum is not just a fantasy, the stuff of science-fiction, it is also a political and medical instrument.Screenshot from Franju, La Tête contre les murs. The truth serum is not just a fantasy...

Should the new career of assistant medical be understood as a return to the Officiers de Santé status ?
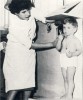
Social paediatrics aim to think of child health holistically, within its environment and to act socially. Social paediatrics aim to think of child health holistically, within its environment and to act...

The Great War marked a second turning point in the history of social policies towards the blind.

Over the course of the 20th century, obesity came to be seen as a public health issue.

In 1852 the criminalisation of abortion is reaffirmed after the Academy of Medicine arrived at a resolution regarding therapeutic abortion.

The lumping together of mental illness and radicalisation leads to negating the latter’s implication in individual and collective history

The Gym Tonic aerobics programme heralded the advent of a new politics of the female body

The notion of neurodiversity appeared at the end of the 90s in an effort to de-pathologize mental illness and combat discrimination.

A body enhancing aesthetic practice, tattooing pertained, in the 19th century, to the world of crime and social deviance.

In 1865 cholera spread from Mecca to the rest of the world, redirecting just-born international health policy’s priorities on Muslim pilgrimage flows.

The 20th century oversaw the development of emergency medicine as a new public health norm.
_max100x100.jpg?objectId=defaultWebContent://9834a0ea-ced1-4de8-ad0c-39dbcb1d6069)
In 19th century Belgium, post-mortem caesarean section turned into a politicized debate.

Did excess mortality among the Great War insane result from a political choice?

Drapotemania exemplifies the existence of psychiatric diagnoses rooted in the political stigmatisation of a social group.

Almost entirely overlooked throughout the 20th century, neglected by contemporary medical manuals, the clitoris has gradually returned centre stage thanks to Western feminism.

From the outset, the measurement of intelligence was as much a scientific as an eminently political endeavour.
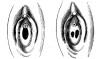
By asserting the hymen, a ubiquitous trait of female anatomy, 19th physicians reinforced the taboos affecting women's sexuality.
DicoPolHiS (standing for dictionnaire politique de l’histoire de la santé, political dictionary of the history of health) is a French initiative which aims to gather the communities of historians, history students and actors of the healthcare system.
This dictionary is both historical and political. Its objective is to examine the social stakes of diagnosis and therapeutic practices since the 18th century to the present. Its historical approach permits to understand the way the social and political notions such as the construction of illnesses, care practices or the human body were defined through history. This dictionary studies concepts such as the relation between the caregiver and the patient, the intervention of citizens in the field of health, the social and political stakes of diagnosis and therapeutic practices.
These standardized notes follow academic rules and are written by academics and advanced history students and a new note is published every week.DicoPolHiS ambitions to become an open reference tool for academic production and to widen and internationalize. This project is led by Hervé Guillemain, historian and professor at Mans University, supported by the research laboratory for history, TEMOS CNRS 9016.
If you are interested in DicoPolHiS, you can follow us on social media (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram) and visit our website: http://dicopolhis.univ-lemans.fr
The best way to help us grow is by sharing the initiative to your historian or health networks. If you are motivated to take part in the project by writing notes for the dictionary, please contact us at dicopolhis@univ-lemans.fr. It might also be for you an opportunity to promote your work on the French and international scenes.